Presenting her third budget, the Minister of Finance, Nirmala Sitharaman, reiterated the government’s vision towards developing an Atma Nirbhar Bharat. Additionally, the honorable FM also categorically divided Part A of the budget into six primary pillars - health and wellbeing, physical & financial capital, infrastructure, inclusive development for aspirational India, reinvigorating human capital, innovation and R&D, minimum government and maximum governance.
Here are the highlights of the Budget 2021 across different sectors.
Health and Wellbeing
Introduction of a new scheme - PM AtmaNirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana, to develop and strengthen primary, secondary, and tertiary care health systems at a total capital outlay of around Rs. 64,180 Crores over a period of 6 years
Launch of the Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) with a total capital outlay of Rs. 2,87,000 Crores over a period of 5 years to ensure universal water supply to over 2.86 crore household tap connections and liquid waste management in 500 AMRUT cities
Implementation of the Urban Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 at a total capital outlay of Rs. 1,41,678 Crores over 5 years from 2021-2026
Allocation of around Rs. 2,217 Crores towards combating air pollution in 42 urban centres
Vehicle scrapping policy to encourage phasing out of old and polluting vehicles: Personal vehicles over the age of 20 years and commercial vehicles over the age of 15 years to undergo fitness tests in automated fitness centres
Rolling out of the pneumococcal vaccine throughout the country
Allocation of around Rs. 35,000 Crores for COVID-19 vaccination in 2021-2022
Here's a quick glimpse of the Government's initiatives to boost the Healthcare sector:

Roadways and Highways Infrastructure
Addition of another 8,500 kilometers of roads to the Bharatmala Pariyojana project by March, 2022
Plan to develop economic corridors in the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, West Bengal, and Assam, among others, as follows:
a. 3,500 km of National Highway works in Tamil Nadu at an investment of Rs. 1.03 Lakh Crores
b. 1,100 km of National Highway works in Kerala at an investment of Rs. 65,000 Crores
c. 675 km of highway works in West Bengal at a cost of Rs. 25,000 Crores
d. Works of more than Rs. 34,000 Crores covering more than 1,300 kms of National Highways to be undertaken in Assam in the coming three years
- Proposal to provide around Rs. 1,18,101 Crores to the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
Railway infrastructure
Plan to commission the Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) and Eastern DFC by June, 2022
Plan to electrify 100% of Broad-Gauge routes by December, 2023
Proposal to provide around Rs. 1,10,055 Crores to the Ministry of Railways
Urban infrastructure
Augmentation of public bus transport services at a cost of around Rs. 18,000 Crores through the Public Private Partnership model
Around 1,016 kilometers of metro and RRTS being constructed in 27 cities
Central counterpart funding to be provided to:
a. Kochi Metro Railway Phase II
b. Chennai Metro Railway Phase II
c. Bengaluru Metro Railway Project Phase 2A and 2B
d. Nagpur Metro Rail Project Phase II
e. Nashik Metro
Power infrastructure
Proposal to introduce a revamped power distribution sector scheme with a capital outlay of Rs. 3,05,984 Crores over a period of 5 years
Proposal to launch a Hydrogen Energy Mission in 2021-22 for generating hydrogen from green power sources
Financial Sector
Consolidation of SEBI Act, 1992, Depositories Act, 1996, Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 and Government Securities Act, 2007 into a rationalized single Securities Markets Code
Increase of permissible FDI limit in the insurance sector to 74% from the existing 49%
Asset Reconstruction Company Limited and Asset Management Company to be set up to resolve stressed assets problem of PSBs
Fiscal deficit for FY22: Budget estimate at 6.8% of GDP
Fiscal deficit for FY21: Revised estimate at 9.5% of GDP
Strategic disinvestment of BPCL, Air India, Shipping Corporation of India, Container Corporation of India, IDBI Bank, BEML, Pawan Hans, Neelachal Ispat Nigam limited etc. to be completed in 2021-22
Two more Public Sector Banks and one General Insurance company to be privatized
IPO of LIC set for 2021-22
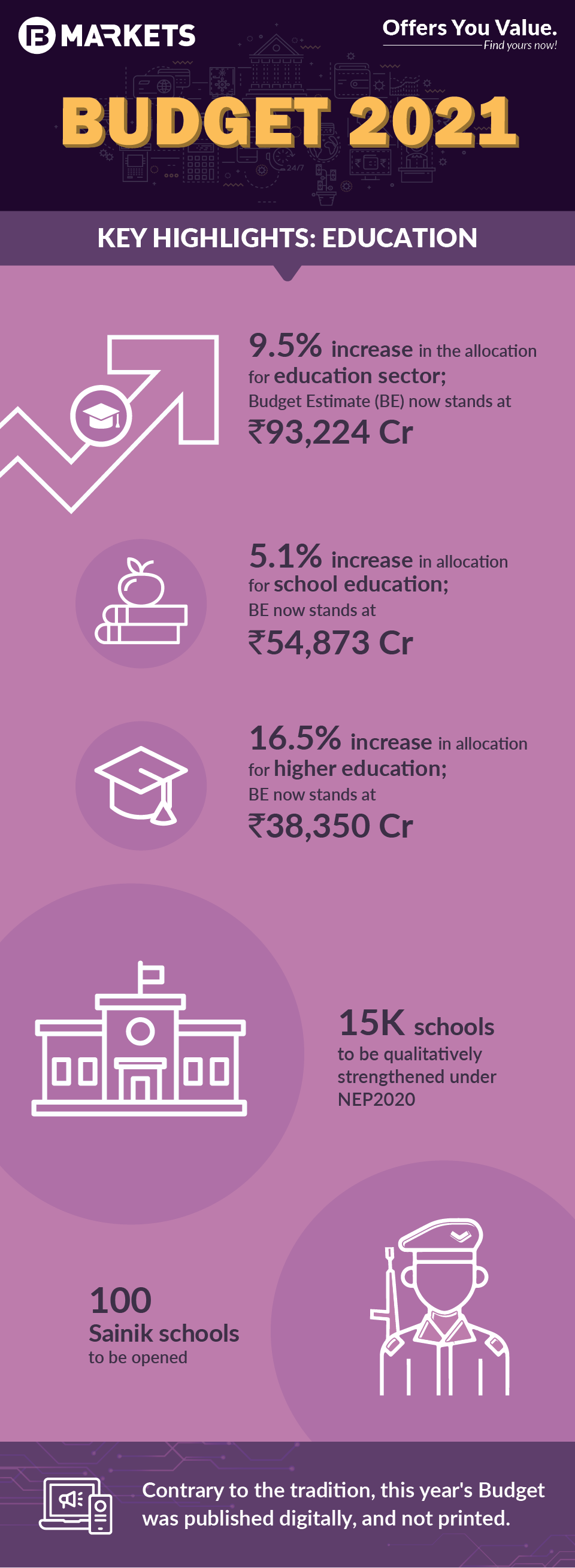
Education Sector
More than 15,000 schools to be qualitatively strengthened to include all components of the National Education Policy
100 new Sainik Schools will be set up in partnership with NGOs/private schools/states
Central University to be set up in Leh for accessible higher education in Ladakh
Over Rs. 3,000 Crores to be provided for realigning the existing scheme of National Apprenticeship Training Scheme (NATS) for providing post-education apprenticeship, training of graduates and diploma holders in Engineering
Take a look at what's in store for the Education sector in Budget 2021:
Fiscal Position
Budget estimates for expenditure in 2021-2022 pegged at Rs. 34.83 Lakh Crores - including Rs. 5.54 Lakh Crores as capital expenditure, an increase of 34.5% over the BE figure of 2020-2021
The Contingency Fund of India to be augmented from Rs. 500 Crores to Rs. 30,000 Crores through Finance Bill
Rs. 1,18,452 Crores provided as Revenue Deficit Grant to 17 states in 2021-2022 on the Finance Commission’s recommendation, as against Rs. 74,340 Crores to 14 States last year
Taxation and Related Proceedings
Senior citizens aged 75 and above - who earn only interest income and pension - are to be exempt from filing income tax returns
Onus to deduct tax on such income for such senior citizens to fall on the paying banks
ULIP proceeds to be taxable as capital gains if the premium paid during any year exceeds Rs. 2.5 Lakhs - except proceeds paid on death
For employees’ contributions to PF exceeding Rs. 2.5 Lakhs a year, interest to be taxable
Reduction in time limit for reopening of income tax assessment from 6 years to 3 years - only in cases of serious tax evasion, where there is evidence of concealment of income of Rs. 50 Lakhs or more in a year, the time limit for reopening income tax assessment to be 10 years
Faceless Income Tax Appellate Tribunal Centre: All communication between the Tribunal and the appellant to be electronic
Rules for removing the hardship of double taxation on NRIs to be notified
Increase in limit for tax audit from Rs. 5 Crore to Rs. 10 Crore
Dividend payment to REIT/ InvIT to be made exempt from TDS
Additional deduction of interest amounting to Rs. 1.5 Lakhs on loan taken to purchase an affordable house to be extended by one more year, up to 31st March 2022
Affordable housing projects to be eligible to avail a tax holiday for one more year – till 31st March, 2022
Here's a quick glance of the updates related to Taxation:

In a Nutshell
Given that the year gone by was a period of unprecedented economic stress, it is understandable that the budget for FY22 has been very liberal in terms of the targeted fiscal deficit. This gives the government ample room to spend enough to bring about economic revival. Also, the focus on healthcare, infrastructure and the financial sector in the Budget 2021 indicates that the government is steadily taking more robust measures to realize their vision of a self-sufficient, Atmanirbhar India.
You may also like to read about:
Presenting her third budget, the Minister of Finance, Nirmala Sitharaman, reiterated the government’s vision towards developing an Atma Nirbhar Bharat. Additionally, the honorable FM also categorically divided Part A of the budget into six primary pillars - health and wellbeing, physical & financial capital, infrastructure, inclusive development for aspirational India, reinvigorating human capital, innovation and R&D, minimum government and maximum governance.
Here are the highlights of the Budget 2021 across different sectors.
Health and Wellbeing
Introduction of a new scheme - PM AtmaNirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana, to develop and strengthen primary, secondary, and tertiary care health systems at a total capital outlay of around Rs. 64,180 Crores over a period of 6 years
Launch of the Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) with a total capital outlay of Rs. 2,87,000 Crores over a period of 5 years to ensure universal water supply to over 2.86 crore household tap connections and liquid waste management in 500 AMRUT cities
Implementation of the Urban Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 at a total capital outlay of Rs. 1,41,678 Crores over 5 years from 2021-2026
Allocation of around Rs. 2,217 Crores towards combating air pollution in 42 urban centres
Vehicle scrapping policy to encourage phasing out of old and polluting vehicles: Personal vehicles over the age of 20 years and commercial vehicles over the age of 15 years to undergo fitness tests in automated fitness centres
Rolling out of the pneumococcal vaccine throughout the country
Allocation of around Rs. 35,000 Crores for COVID-19 vaccination in 2021-2022
Here's a quick glimpse of the Government's initiatives to boost the Healthcare sector:



